4.10. Union node
Number of inputs: 2 or more.
Number of outputs: 1.
- Definition
A union node lets you add multiple input datasets (stacking), corresponding to new rows (union in the SQL sense).
- Configuration
A union node is used to combine two or more datasets.
Each dataset is added at the end of the previous dataset.
Three stacking strategies are available:
Use the first dataset as a reference:
the first dataset determines the names and types of the fields in the output dataset. This option will trigger an error if the number OR type of the input fields do not match.
Union of input fields :
if, for example, the first dataset has fields A, B and C and the second dataset has fields B, C & D then the output dataset will have the fields A, B, C & D. Fields with types that do not match will be converted to text.
Intersection of input fields: if, for example, the first dataset has fields A, B and C and the second has fields B, C & D then the output dataset will have the fields B & C. Fields with types that do not match will be converted to text.
Within the union node configurator you can also specify the field of provenance (by name). This is a field that will be added after the union and will indicate the dataset of provenance (or origin) of each record:

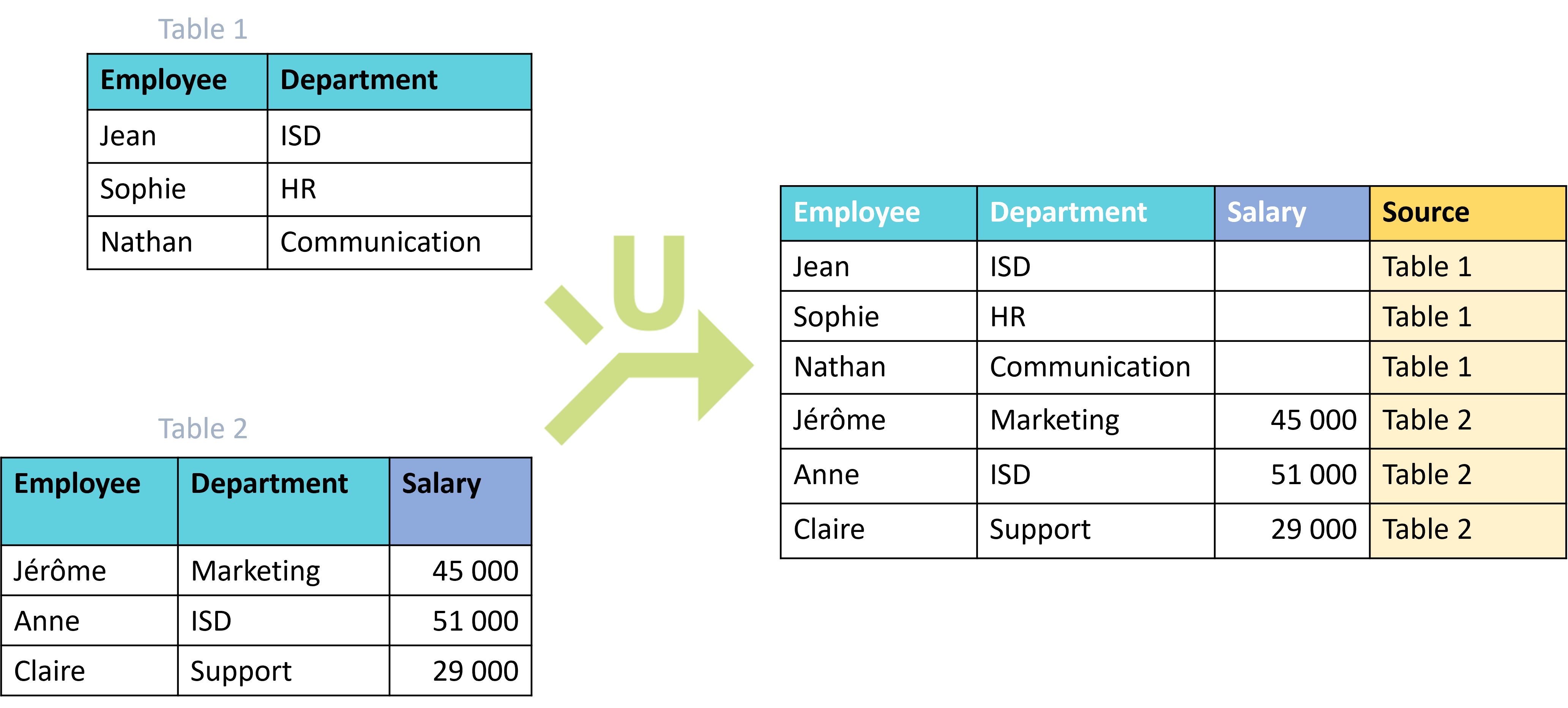
- Visual example
In this example, a field union strategy is set up with an additional provenance field (Origin):
- Practical examples
Note
Example 1: Use First Dataset as Reference
Before operation:
Dataset 1:
A (Number)
B (Text)
C (Date)
1
Alpha
2023-01-01
2
Beta
2023-02-02
Dataset 2:
D (Number)
E (Text)
F (Date)
3
Gamma
2023-01-03
4
Delta
2023-01-04
Configuration du nœud :
Union Kind:
Use First Dataset as ReferenceDataset source field name:
EMPTY
After operation:
Combined Dataset:
A (Number)
B (Text)
C (Date)
1
Alpha
2023-01-01
2
Beta
2023-02-02
3
Gamma
2023-01-03
4
Delta
2023-01-04
The union works because:
Columns A and D have the same type.
Columns B and E have the same type.
Columns C and F have the same type.
The column names of the first dataset are retained, as this is the reference dataset.
Note
Example 2: Union of Input Fields
Before operation:
Dataset 1:
A
B
C
1
X
2023-01-01
Dataset 2:
B
C
D
Y
2023-02-02
100
Configuration du nœud :
Union Kind:
Union of Input FieldsDataset source field name:
EMPTY
After operation:
Combined Dataset:
A
B
C
D
1
X
2023-01-01
NULL
NULL
Y
2023-02-02
100
The resulting dataset includes all fields from both input datasets. Missing values are represented as
NULL.Note
Example 3: Intersection of Input Fields
Before operation:
Dataset 1:
A
B
C
1
X
2023-01-01
Dataset 2:
B
C
D
Y
2023-02-02
100
Configuration du nœud :
Union Kind:
Intersection of Input FieldsDataset source field name:
EMPTY
After operation:
Combined Dataset:
B
C
X
2023-01-01
Y
2023-02-02
Seuls les champs communs à tous les jeux de données en entrée (B et C) sont inclus dans le jeu de données résultant.
Note
Example 4: Data lineage
Automatically add a column indicating the origin of the record.
Before operation:
Dataset 1:
A
B
1
X
2
Y
Dataset 2:
A
C
3
Z
4
W
Configuration du nœud :
Union Kind:
Union of Input FieldsDataset source field name:
Source(Lineage)
After operation:
If the Data set source field name is not empty, the output dataset will have an additional column named “Source” which indicates the origin of each record:
Combined Dataset:
A
B
C
Source
1
X
NULL
Dataset 1
2
Y
NULL
Dataset 1
3
NULL
Z
Dataset 2
4
NULL
W
Dataset 2