4.5. Filter node
If you want to learn more about this feature, an e-learning tutorial is available below:
Using Filter Nodes
Filter nodes are awesome in what you can do with them. Did you know you could set up several outputs with a single one?
Advanced usage of the preparation editor : all about filtering
This video presents how to use filters in the preparation editor. These can be extremely useful for looking at your data and exploring it. Furthermore it can also help in cases where you would quickly like to apply transformations only on a subset of your data. Both uses are illustrated and should help you become very proficient with this tool.
4.5.1. Description
Number of inputs: 1.
Number of outputs: 1 or more.
- Definition
A filter node lets you select the fields and records to be sent to each of its outputs.
- Configuration
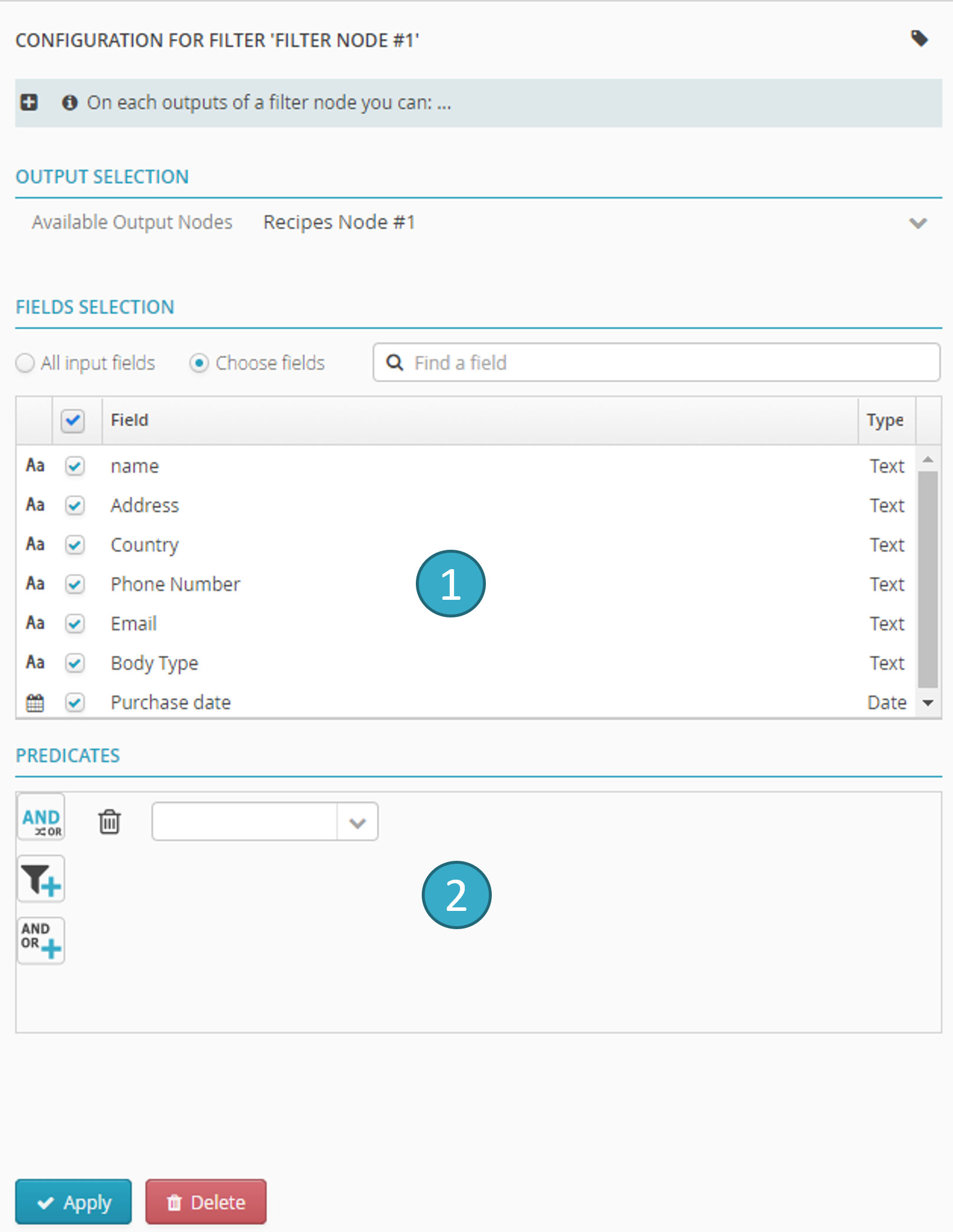
For each filter node output, you can:
Select a subset of fields and rearrange them (by dragging and dropping in the columns list)
 .
.Select a subset of records by setting conditions in the predicate zone
 .
.
Tip
If no condition is assigned to the last output link of a filter node, that last link will retrieve all the records that failed to meet any of the previous output conditions.
- Visual example
-
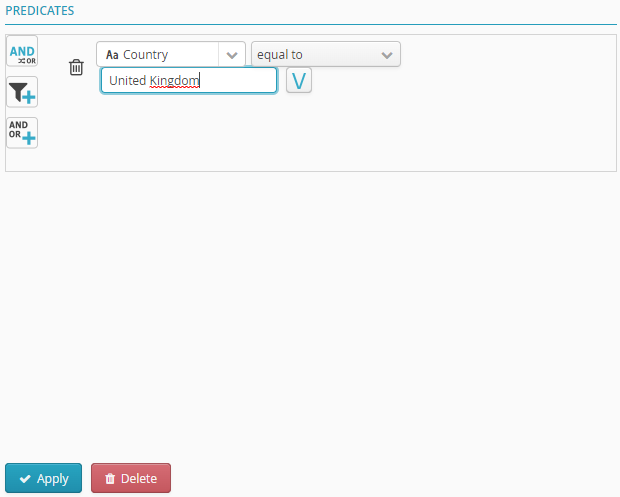
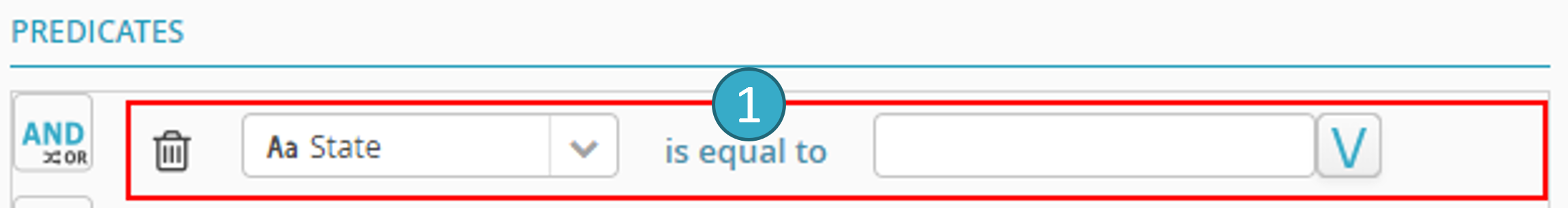
This example shows how conditions are added to configure filtering.
This filter node will retrieve values equal to United Kingdom from the Country column.
- Practical examples
Note
Example 1: Basic Filtering by Column Value
Before operation:
ID
Name
Age
Country
1
Alice
30
USA
2
Bob
25
Canada
3
Charlie
35
USA
4
Diana
40
United Kingdom
In the configuration zone of the filter node:
Predicate: Country = “USA”
Selected Columns: ID, Name, Age
Select All: True
After operation
ID
Name
Age
1
Alice
30
3
Charlie
35
Note
Example 2: Multiple Output Configurations with Fallback
Before operation:
ID
Name
Age
Country
1
Alice
30
USA
2
Bob
25
Canada
3
Charlie
35
USA
4
Diana
40
United Kingdom
In the configuration zone of the filter node:
Output 1:
Predicate: Age > 30
Selected Columns: ID, Name
Output 2:
Predicate: Country = “Canada”
Selected Columns: Name, Age
Output 3 (Fallback):
Predicate: (No explicit predicate; falls back to rows not meeting other predicates)
After operation
Output 1:
ID
Name
3
Charlie
4
Diana
Output 2:
Name
Age
Bob
25
Output 3:
ID
Name
Age
Country
1
Alice
30
USA
4.5.2. Configuration examples
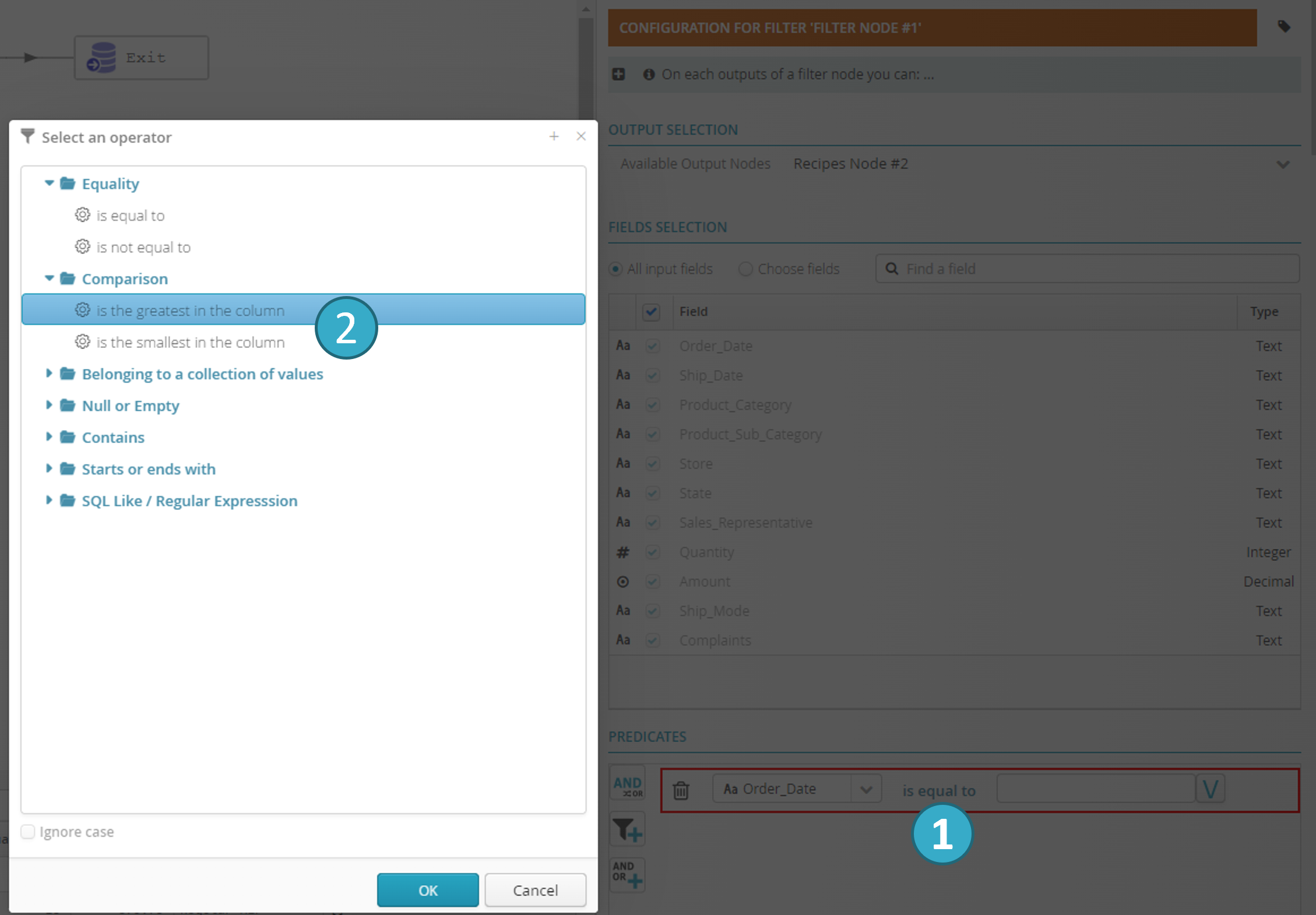
4.5.2.1. Is the greatest or smallest in the column
You may wish to filter a dataset by the greatest or smallest value in a column.
A classic example of this is retrieval of the latest rows added to a dataset. By applying the ‘is the greatest in the column’ filter to the Date of Purchase column, only recently imported rows will be retrieved.
In the configuration zone of the filter node:
4.5.2.2. Lookup function (search in the column of a table outside the flow)
You can also use the filter node to search (lookup) a column in another dataset to check a condition:
Click the predicates operator  .
.
You can select a predicates operator in the dialog window that will open.
There are four operators for looking up condition values in the column of another table  :
:
Is in the column.
Is not in the column.
Contains at least one column item.
Contains no column items.

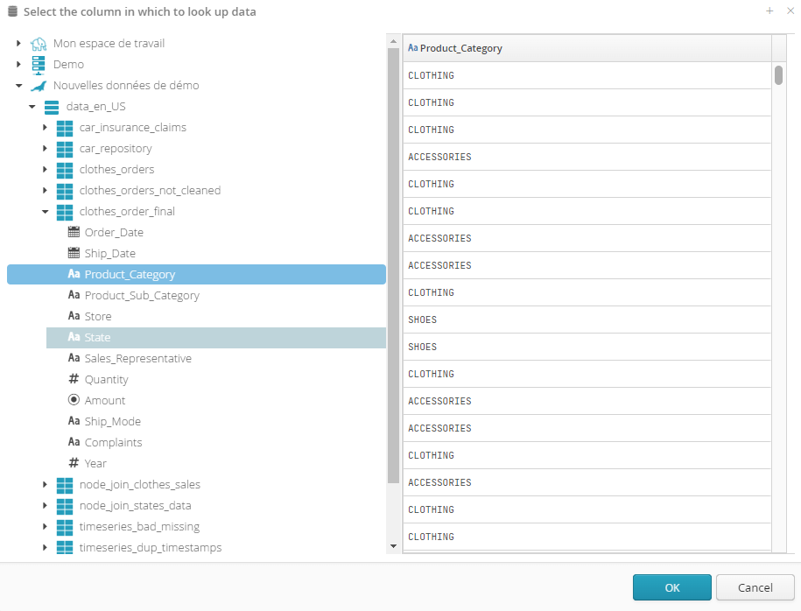
Once one of the four operators has been selected, click the button to the right of the text box  :
:

Now just select the column to be searched for data for the right section of the condition:
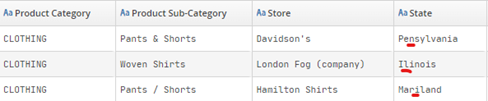
The example above shows the retrieval of rows in our dataset whose status is not on the reference list (us_states.csv) clearly because of spelling mistakes: