4.8. Join node
Number of inputs: 2 or more.
Number of outputs: 1.
- Definition
A join node lets you make an SQL join using multiple input datasets.
- Configuration
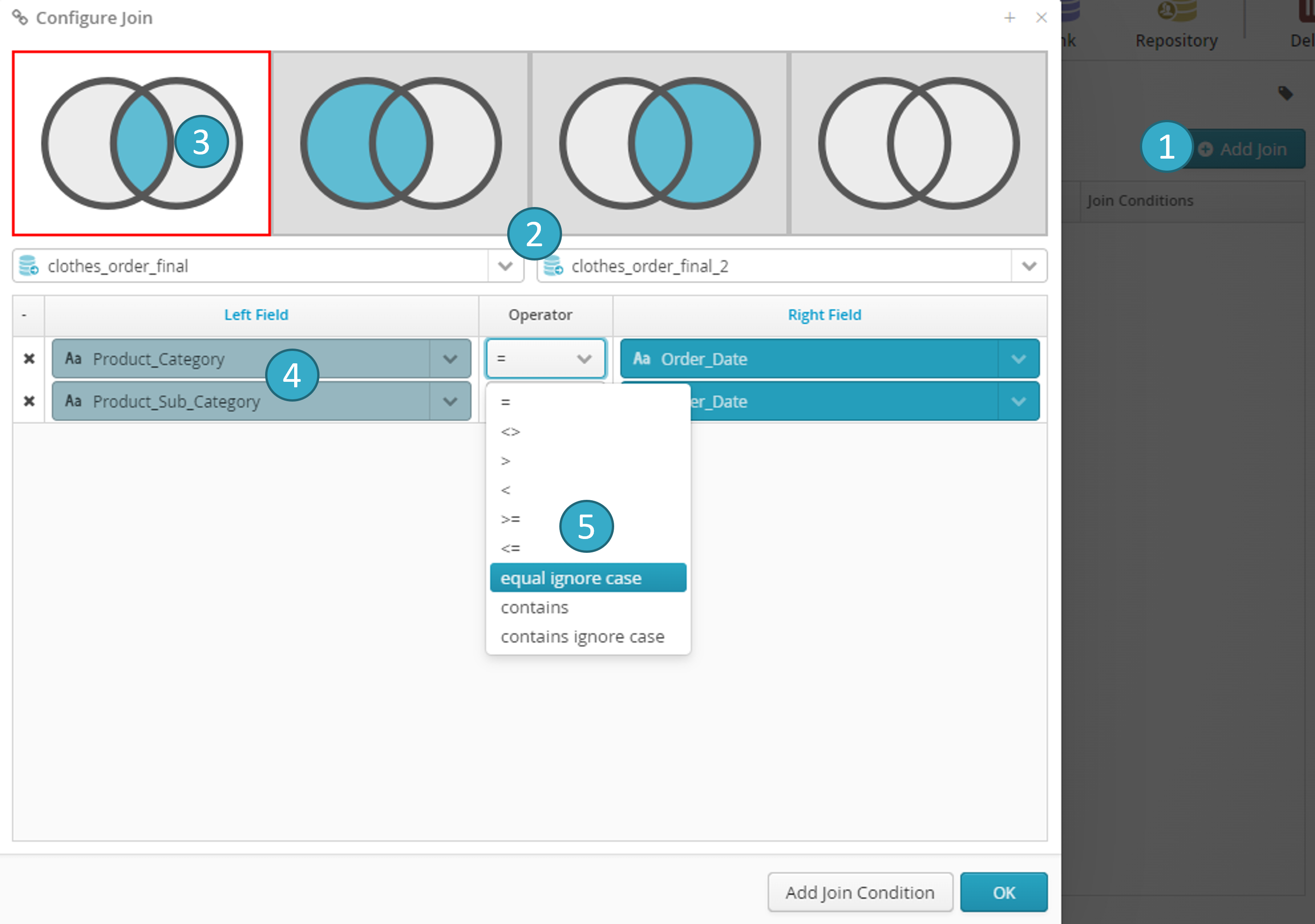
When the join node is connected at input to at least two nodes, you can click Add a join
 to configure for each pair of input datasets
to configure for each pair of input datasets  involved in the join:
involved in the join:- Visual example
Four possible types of join:
Based on the following data and making the join at the make field:
Make
Model
Ford
Focus
Citroen
Picasso
Renault
Megane
Nissan
GT-R
Make
Country
Renault
France
Toyota
Japan
Ford
USA
Inner: keeps data whose records in the first dataset match those in the second dataset:
Make
Model
Country
Ford
Focus
USA
Renault
Megane
France
Left (or Left Outer): keeps all the data from the first dataset by matching its records with those of the second dataset. If no match is found, the fields corresponding with the second dataset will be blank:
Make
Model
Country
Ford
Focus
USA
Citroen
Picasso
<null>
Renault
Megane
France
Nissan
GT-R
<null>
Right (or Right Outer): keeps all the data from the second dataset by matching its records with those of the first dataset. If no match is found, the fields corresponding with the first dataset will be blank:
Make
Model
Country
Renault
Megane
France
Toyota
<null>
Japan
Ford
Focus
USA
Full (or Full Outer): keeps all data from each dataset (first and second) by matching its records with those of the other dataset. If no match is found in any dataset, the corresponding fields will be blank:
Make
Model
Country
Ford
Focus
USA
Citroen
Picasso
<null>
Renault
Megane
France
Nissan
GT-R
<null>
Toyota
<null>
Japan
- Practical examples
Note
Example 1: Inner Join
Before operation:
Table A:
customer_id
name
1
Alice
2
Bob
3
Carol
Table B:
customer_id
order_id
1
1001
2
1002
4
1003
Node Configuration:
Join Kind: Inner Join
Join Condition:
TableA.customer_id = TableB.customer_id
After operation:
customer_id
name
order_id
1
Alice
1001
2
Bob
1002
Note
Example 2: Left Outer Join
Before operation:
Table A:
customer_id
name
1
Alice
2
Bob
3
Carol
Table B:
customer_id
order_id
1
1001
2
1002
4
1003
Node Configuration:
Join Kind: Left Outer Join
Join Condition:
TableA.customer_id = TableB.customer_id
After operation:
customer_id
name
order_id
1
Alice
1001
2
Bob
1002
3
Carol
NULL
Note
Example 3: Right Outer Join
Before operation:
Table A:
customer_id
name
1
Alice
2
Bob
3
Carol
Table B:
customer_id
order_id
1
1001
2
1002
4
1003
Node Configuration:
Join Kind: Right Outer Join
Join Condition:
TableA.customer_id = TableB.customer_id
After operation:
customer_id
name
order_id
1
Alice
1001
2
Bob
1002
4
NULL
1003
Note
Example 4: Full Outer Join
Before operation:
Table A:
customer_id
name
1
Alice
2
Bob
3
Carol
Table B:
customer_id
order_id
1
1001
2
1002
4
1003
Node Configuration:
Join Kind: Full Outer Join
Join Condition:
TableA.customer_id = TableB.customer_id
After operation:
customer_id
name
order_id
1
Alice
1001
2
Bob
1002
3
Carol
NULL
4
NULL
1003